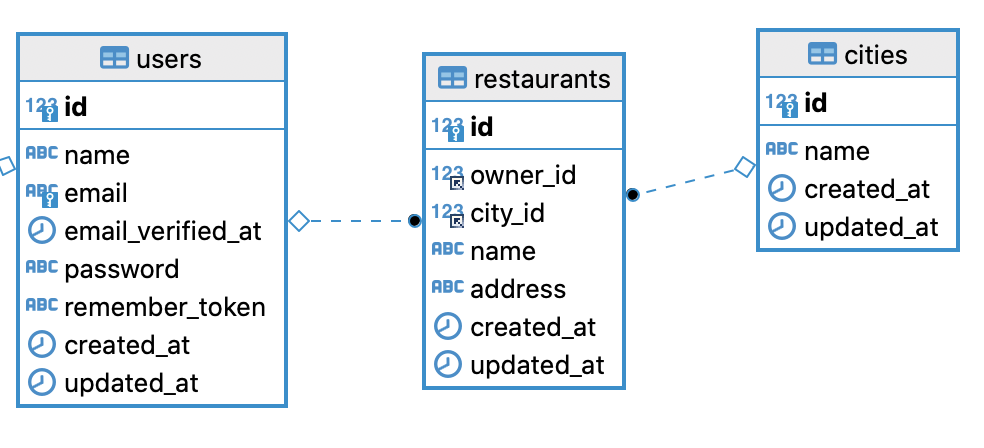
In this lesson, we will prepare DB schema and Models for managing Restaurants by the administrator. The database schema will look as follows:
Cities table
- id
- name
Restaurants table
- id
- owner_id - user id which the restaurant belongs to
- city_id - restaurants will belong to a city
- name
- address
Here's the schema we're aiming for:
Create a City Model
First, let's create a City model with Migration and Seeder:
php artisan make:model City -msdatabase/migrations/2023_05_31_000005_create_cities_table.php
public function up(): void{ Schema::create('cities', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->string('name'); $table->timestamps(); });}And update CitySeeder with the following content:
database/seeders/CitySeeder.php
namespace Database\Seeders; use App\Models\City;use Illuminate\Database\Console\Seeds\WithoutModelEvents;use Illuminate\Database\Seeder; class CitySeeder extends Seeder{ /** * Run the database seeds. */ public function run(): void { $cities = ['Aalborg', 'Aarhus', 'Aba', 'Abeokuta', 'Abovyan', 'Abuja', 'Accra', 'Adana', '...', 'Zaria', 'Zenica', 'Zhodzina', 'Zilina', 'Zvolen', 'Zürich', 'Other']; foreach ($cities as $city) { City::create(['name' => $city]); } }}You can customize available cities as you want.
To seed cities, update the DatabaseSeeder file by adding CitySeeder::class:
database/seeders/DatabaseSeeder.php
public function run(): void{ $this->call([ PermissionSeeder::class, RoleSeeder::class, CitySeeder::class, UserSeeder::class, ]);}We insert CitySeeder before UserSeeder because we need cities present if we seed fake user users with restaurants.
Create a Restaurant Model
Now it is time to create a Restaurant Model with Migration:
php artisan make:model Restaurant -mThen update restaurants Migration:
database/migrations/2023_05_31_000006_create_restaurants_table.php
use App\Models\City; public function up(): void{ Schema::create('restaurants', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->foreignId('owner_id')->references('id')->on('users'); $table->foreignIdFor(City::class)->constrained(); $table->string('name'); $table->text('address'); $table->timestamps(); });}Because we use a custom column name as owner_id, we can't just use the constrained() method. We need to specify what column on which table it references: references('id')->on('users').
Then update the Restaurant Model by specifying $fillable columns and add relationships:
app/Models/Restaurant.php
namespace App\Models; use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Factories\HasFactory;use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Relations\BelongsTo; class Restaurant extends Model{ use HasFactory; protected $fillable = ['city_id', 'name', 'address']; public function owner(): BelongsTo { return $this->belongsTo(User::class, 'owner_id'); } public function city(): BelongsTo { return $this->belongsTo(City::class); }}Finally, add the relationship to the Restaurant Model on the User Model:
app/Models/User.php
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Relations\HasOne; // ... public function restaurant(): HasOne{ return $this->hasOne(Restaurant::class, 'owner_id');}Ok, so we have our DB schema for restaurants, owners, and cities.

In the next lesson, we will continue with Controller for admin to view/manage restaurants.
