Caching with Redis is one of the common requirements in Laravel job descriptions. But it's not complicated at all, this tutorial will show you the fundamentals.
Here's a simple example on how to use Redis in Laravel for caching Eloquent queries.
1. Redis server: install/launch
Redis is not a Laravel-specific system, it is installed separately, just follow its official installation instructions.
Then, just launch it with the command redis-server.
2. Install Redis PHP Extension
Ensure you have the Redis PHP extension installed:
For Ubuntu based systems:
sudo apt-get install redis php8.4-redissudo systemctl restart php8.4-fpm.serviceIf needed, replace the PHP version with the version used in your system.
3. Install Predis Package
Predis is a flexible and feature-complete Redis client for PHP. Install it via Composer:
composer require predis/predis4. Configure Redis in Laravel
Change the CACHE_STORE to redis in the .env file:
CACHE_STORE=redisEdit the .env file to change Redis server configuration if not using the default values:
REDIS_CLIENT=phpredisREDIS_HOST=127.0.0.1REDIS_PASSWORD=nullREDIS_PORT=63795. Use Redis in Laravel for Caching
5.1 Cache an Eloquent Query
Suppose you have an Eloquent query like this:
$users = User::where('active', 1)->get();To cache this query result with Redis:
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Cache; $users = Cache::remember('active_users', 60, function () { return User::where('active', 1)->get();});Here, 'active_users' is the cache key, 60 is the number of seconds to cache the result, and the closure fetches the users when the cache is not found.
5.2 Clear Cache
To clear the cached result:
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Cache; Cache::forget('active_users');6. Display Cached Data
Here's a simple example to display active users using caching:
- Create a route in
web.php:
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Cache;use App\Models\User; Route::get('/active-users', function () { $users = Cache::remember('active_users', 60, function () { return User::where('active', 1)->get(); }); return view('active_users', ['users' => $users]);});- Create a view
active_users.blade.php:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Active Users</title></head><body> <h1>Active Users</h1> <ul> @foreach($users as $user) <li>{{ $user->name }}</li> @endforeach </ul></body></html>Now, when you visit /active-users in your browser, it will fetch and display active users from the database and cache the result for 60 seconds.
7. Check Current Cache
If you want to see what values are cached at the moment, you can do it with a tool called RedisInsight.
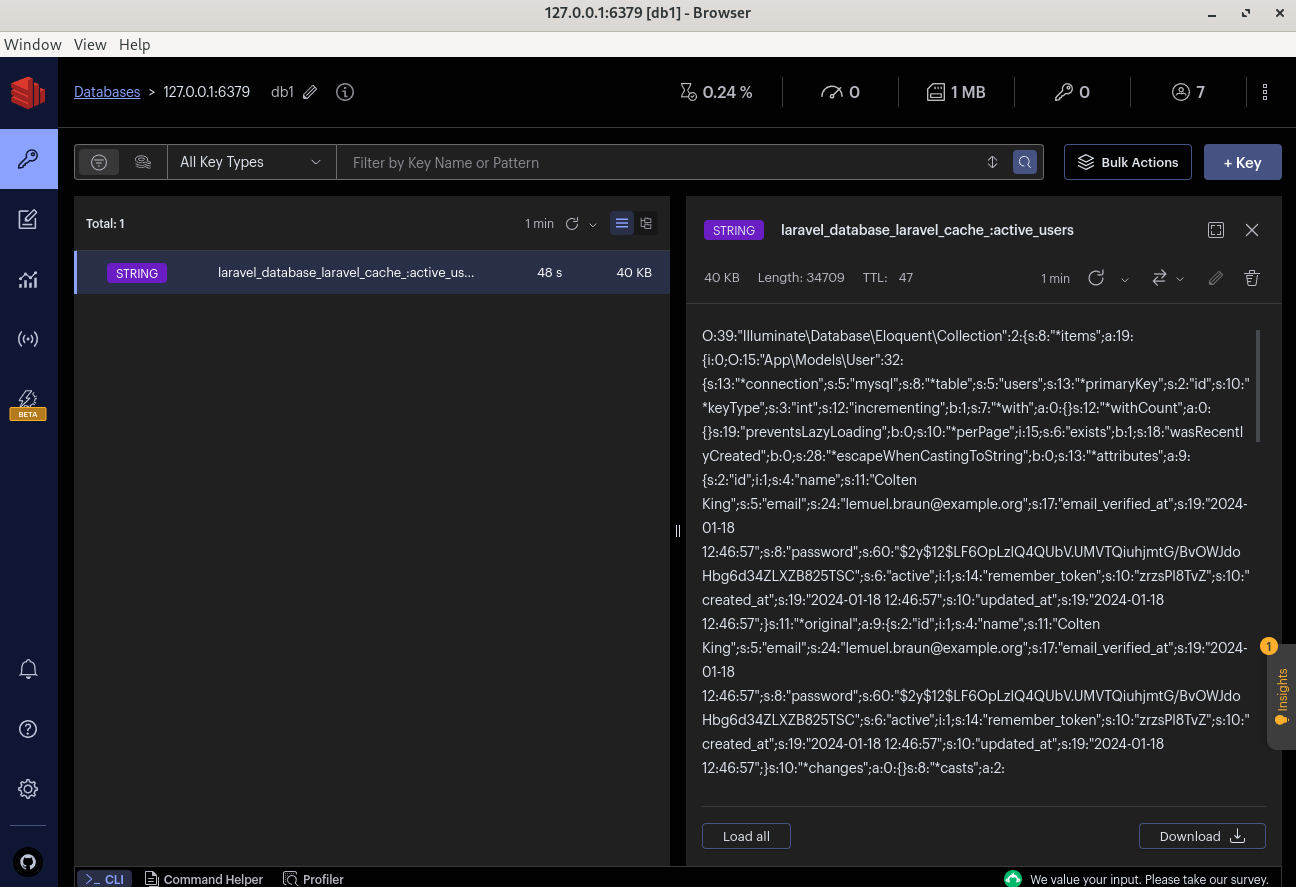
You can read much more about Redis in our premium tutorial Redis in Laravel 101: Main Things You Need to Know.

Just a quick correction for the Cache::remember call. "60 is the number of minutes" is not true. It's the number of seconds to cache.
See: https://laravel.com/docs/10.x/cache#retrieve-store
Thanks. Updated article
It has a minor typo. 60 is the number of seconds.