It's time to make our first resource - Customer.
In this lesson, we will:
- Create DB structure for Customers: Model/Migration
- Create Factories/Seeds for testing data
- Generate Filament Resource directly from the DB structure
- Hide the
deleted_atcolumn from the table - Merge
first_nameandlast_nameinto one table column
We will have the following fields in our Customer resource:
-
id -
first_name -
last_name -
email -
phone_number -
description -
timestamps -
soft deletes
Creating Customer Database
Our first step is to create our Database table and Model:
Migration
Schema::create('customers', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->string('first_name')->nullable(); $table->string('last_name')->nullable(); $table->string('email')->nullable(); $table->string('phone_number')->nullable(); $table->text('description')->nullable(); $table->timestamps(); $table->softDeletes();});As you can see, we have made all of our fields nullable. We don't know if the customer will have all these fields or just some. So, we leave some room for flexibility for our users.
Now, let's create the Model:
app/Models/Customer.php
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Factories\HasFactory;use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\SoftDeletes; class Customer extends Model{ use SoftDeletes; use HasFactory; protected $fillable = [ 'first_name', 'last_name', 'email', 'phone_number', 'description', ];}Since we use the HasFactory trait, we should create a factory for our Customer model. It will be helpful for testing purposes!
php artisan make:factory CustomerFactoryThen, we will add the fields to our factory:
database/factories/CustomerFactory.php
use App\Models\Customer;use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Factories\Factory; /** * @extends Factory<Customer> */class CustomerFactory extends Factory{ protected $model = Customer::class; /** * Define the model's default state. * * @return array<string, mixed> */ public function definition(): array { return [ 'first_name' => $this->faker->firstName(), 'last_name' => $this->faker->lastName(), 'email' => $this->faker->unique()->safeEmail(), 'phone_number' => $this->faker->phoneNumber(), 'description' => $this->faker->text(), ]; }}Now, we can create a seeder for our Customer model:
database/seeders/DatabaseSeeder.php
use App\Models\Customer; // ... public function run(): void{ // ... Customer::factory() ->count(10) ->create();}We can test our seeder by running:
php artisan migrate:fresh --seedThis command should clear our database, migrate it from scratch, and seed it with our defined seeders. Once it's done, we should be able to see our customers in the database:

This should be enough for us to test our Filament resource. Let's create it!
Creating Customer Resource
To create the base resource, we can use the Filament generator:
php artisan make:filament-resource Customer --generateAfter running this command, we should see a few new files in our project:

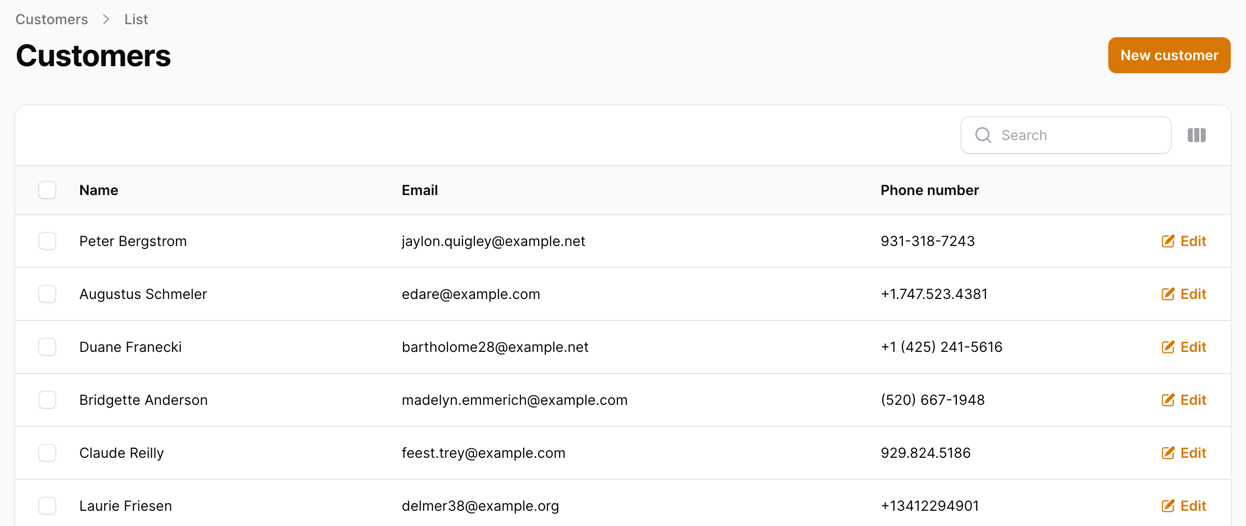
These files contain all the necessary code to create a resource in Filament, meaning that we can open our browser and visit our Customers page:
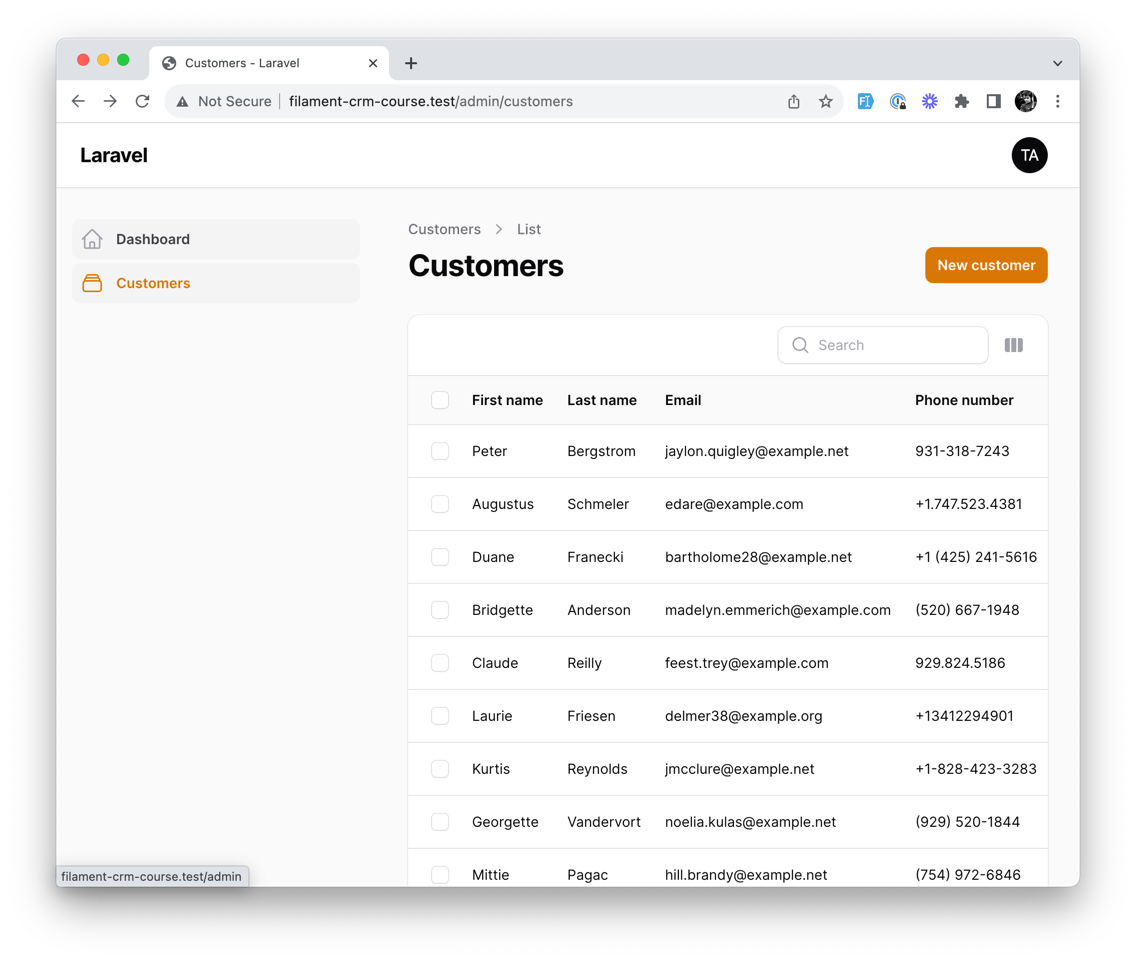
How cool is that? We just created a model, ran a single command, and Filament generated a resource for us! But let's dive deeper into what we just created and modify some things to make it more useful:
Modifying Customer Resource
Our primary focus should be app/Filament/Resources/CustomerResource.php as this file is responsible for Table and Form generation. Let's take a look at it:
app/Filament/Resources/CustomerResource.php
use App\Filament\Resources\CustomerResource\Pages;use App\Filament\Resources\CustomerResource\RelationManagers;use App\Models\Customer;use Filament\Forms;use Filament\Forms\Form;use Filament\Resources\Resource;use Filament\Tables;use Filament\Tables\Table;use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Builder;use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\SoftDeletingScope; class CustomerResource extends Resource{ // ... public static function form(Form $form): Form { // This is where we define what fields we want to have in our form return $form ->schema([ Forms\Components\TextInput::make('first_name') ->maxLength(255), Forms\Components\TextInput::make('last_name') ->maxLength(255), Forms\Components\TextInput::make('email') ->email() ->maxLength(255), Forms\Components\TextInput::make('phone_number') ->tel() ->maxLength(255), Forms\Components\Textarea::make('description') ->maxLength(65535) ->columnSpanFull(), ]); } public static function table(Table $table): Table { // This is where we define our table columns, filters, actions, and any other table-related things return $table ->columns([ Tables\Columns\TextColumn::make('first_name') ->searchable(), Tables\Columns\TextColumn::make('last_name') ->searchable(), Tables\Columns\TextColumn::make('email') ->searchable(), Tables\Columns\TextColumn::make('phone_number') ->searchable(), Tables\Columns\TextColumn::make('created_at') ->dateTime() ->sortable() ->toggleable(isToggledHiddenByDefault: true), Tables\Columns\TextColumn::make('updated_at') ->dateTime() ->sortable() ->toggleable(isToggledHiddenByDefault: true), Tables\Columns\TextColumn::make('deleted_at') ->dateTime() ->sortable(), ]) ->filters([ // ]) ->actions([ Tables\Actions\EditAction::make(), ]) ->bulkActions([ Tables\Actions\BulkActionGroup::make([ Tables\Actions\DeleteBulkAction::make(), ]), ]); } // ...}Table Modifications
But how can we modify this? Well, let's start with something simple - our Customers table has a deleted_at column that we want to hide:
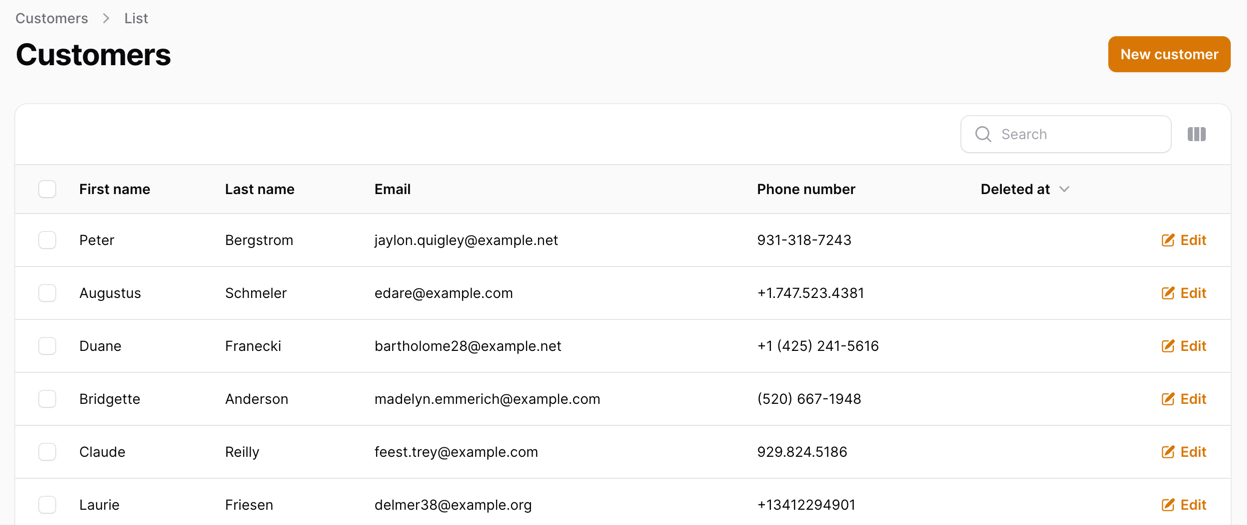
To hide it, we can borrow some code from the created_at column like so:
app/Filament/Resources/CustomerResource.php
use App\Filament\Resources\CustomerResource\Pages;use App\Filament\Resources\CustomerResource\RelationManagers;use App\Models\Customer;use Filament\Forms;use Filament\Forms\Form;use Filament\Resources\Resource;use Filament\Tables;use Filament\Tables\Table;use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Builder;use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\SoftDeletingScope; class CustomerResource extends Resource{ // ... public static function table(Table $table): Table { return $table ->columns([ Tables\Columns\TextColumn::make('first_name') ->searchable(), Tables\Columns\TextColumn::make('last_name') ->searchable(), Tables\Columns\TextColumn::make('email') ->searchable(), Tables\Columns\TextColumn::make('phone_number') ->searchable(), Tables\Columns\TextColumn::make('created_at') ->dateTime() ->sortable() ->toggleable(isToggledHiddenByDefault: true), Tables\Columns\TextColumn::make('updated_at') ->dateTime() ->sortable() ->toggleable(isToggledHiddenByDefault: true), Tables\Columns\TextColumn::make('deleted_at') ->dateTime() ->sortable() ->toggleable(isToggledHiddenByDefault: true), ]) ->filters([ // ]) ->actions([ Tables\Actions\EditAction::make(), ]) ->bulkActions([ Tables\Actions\BulkActionGroup::make([ Tables\Actions\DeleteBulkAction::make(), ]), ]); } // ...}Now, if we refresh our page, we should see that the column is hidden:
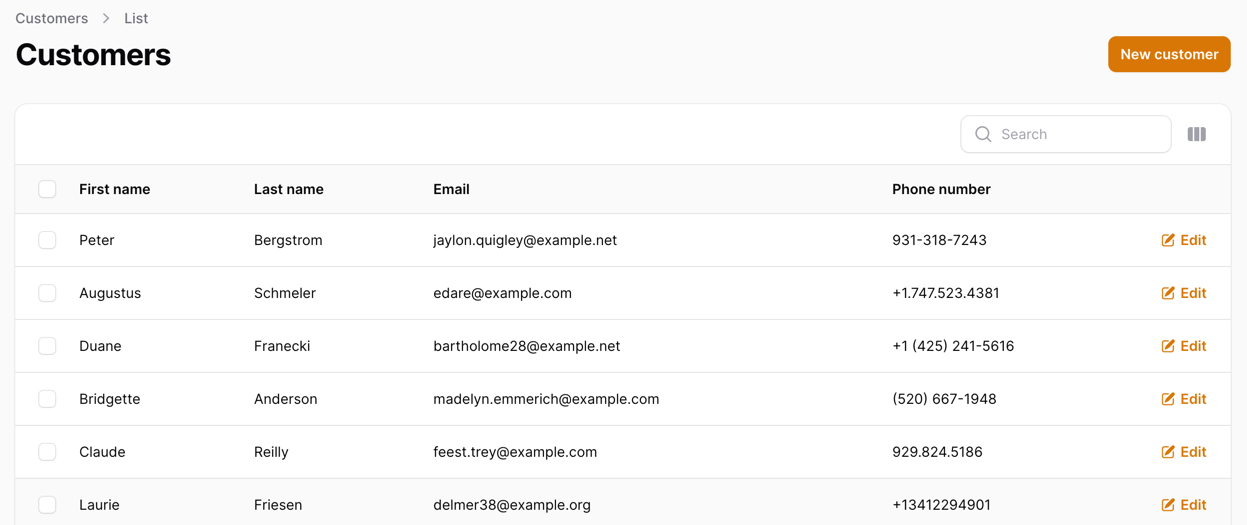
But that's not all! We still want a Full Name column in our table, not just the first_name and last_name columns. To do that, we need to create a new column, Name and remove the first_name and last_name columns:
app/Filament/Resources/CustomerResource.php
// ... public static function table(Table $table): Table{ return $table ->columns([ Tables\Columns\TextColumn::make('first_name') // We are setting the column label to "Name" ->label('Name') // This function allows us to format the column value // In this case, we are concatenating first_name and last_name ->formatStateUsing(function ($record) { return $record->first_name . ' ' . $record->last_name; }) // This function allows us to inform Filament that this column is searchable // And also define in which columns the search should be performed // In this case - first_name and last_name columns ->searchable(['first_name', 'last_name']), Tables\Columns\TextColumn::make('first_name') ->searchable(), Tables\Columns\TextColumn::make('last_name') ->searchable(), // ... ]) ->filters([ // ]) ->actions([ Tables\Actions\EditAction::make(), ]) ->bulkActions([ Tables\Actions\BulkActionGroup::make([ Tables\Actions\DeleteBulkAction::make(), ]), ]);}// ...And this is how our table looks now:

And the search also works if we search for a last name:
Or even if we search for a full name:
Form Modifications
Next, let's check that our form is working as expected, too. Open the form and try to create a new customer:
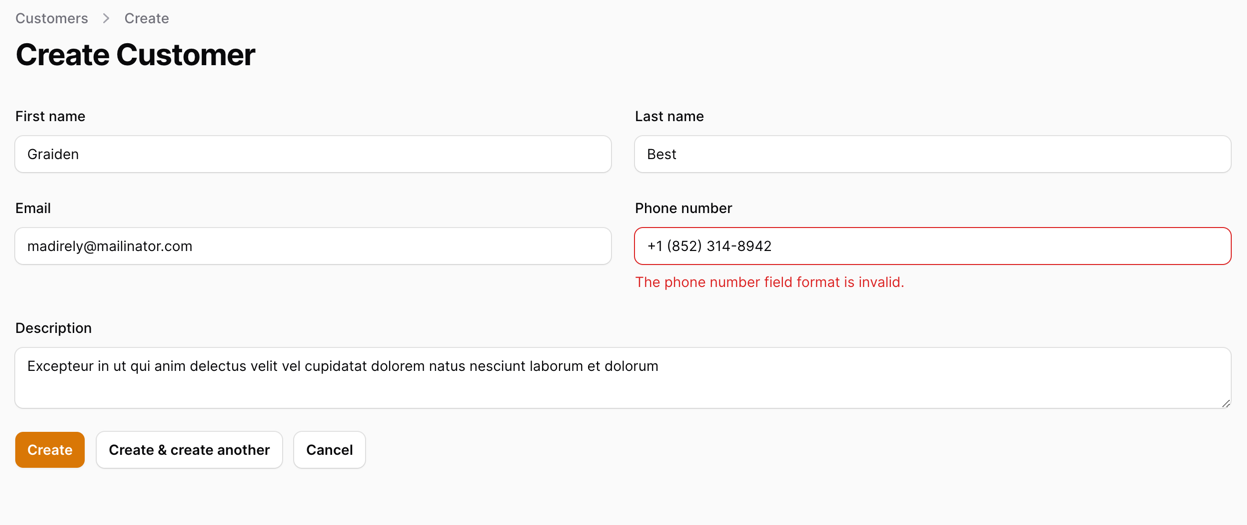
As you can see, even if we enter a valid phone number - we still get an error. This is because we have a validation rule for our phone number field:
app/Filament/Resources/CustomerResource.php
public static function form(Form $form): Form{ return $form ->schema([ // ... Forms\Components\TextInput::make('phone_number') // This is the validation rule that causes the error. We will remove it for now ->tel() ->maxLength(255), // ... ]);}Now, once the rule is removed, we can create a new customer:
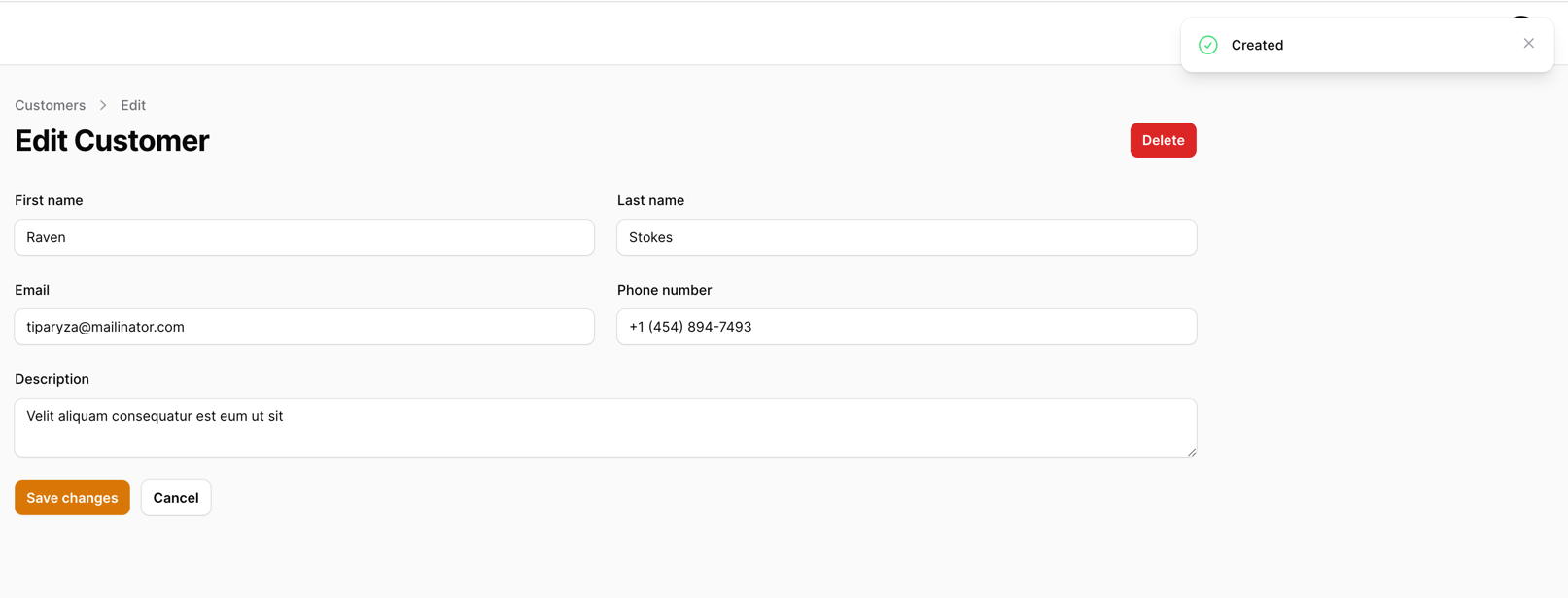
As you can see, we have successfully created a new customer!
This is it! You have successfully created your first resource in Filament! Next, we will create a new resource - Lead Sources.

Why removing the validation rule for phone. Does this means that we allow user to input any data without validation? I guess the phone validation is important from my perspective.
Phone validation comes with it's own set of rules and formatting. It does not really match other common formats, so we removed it and left for everyone to decide on it :)
Okay, can we explore validation rules with filament in upcoming course on filament. Thanks
Will take a look at what we can do here!
Most likely we will have a section on custom rule creation to fit fields like phone number in
Great!
I have a suggestion for the phone validation
'phone' => 'required|regex:/^([0-9\s-+()]*)$/|min:10',
'mobile' => 'regex:/^([0-9\s-+()]*)$/|min:10|nullable',
This is what I normaly use.
Phone validation is tricky, as each country might have different rules for formatting. In any case, if it works - it works!
As of Filament 3.0.94 the error with the phone number is no more I am not getting the error as of today 11/12/2023 doing a restart with github