We've been focusing on optimizing Eloquent for data retrieval, but seeding large amounts of data efficiently is equally important.
This lesson examines strategies to significantly improve the performance of your Laravel database seeders.
The Challenge: Seeding Large Datasets
Consider a scenario where we need to seed:
- Countries
- Companies
- Positions
- Employees (20,000 records)
Each employee belongs to a country, a position, and a company.
Approach 1: Traditional For Loop with Eloquent Create
The conventional approach using Eloquent's create() in a loop:
public function run(){ for ($i = 0; $i < 20000; $i++) { Employee::create([ 'name' => fake()->name(), 'company_id' => rand(1, 100), 'country_id' => rand(1, 100), 'position_id' => rand(1, 20) ]); }}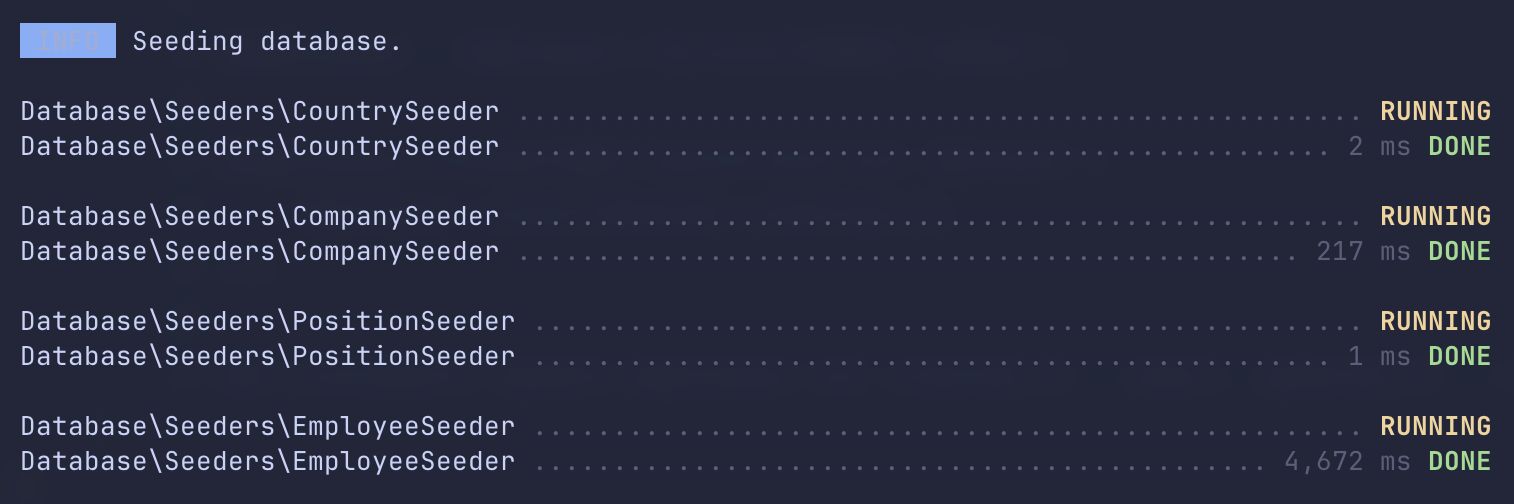
Other seeders are really quick but for employee it took 4,6 seconds for 20,000 employees.
This approach is slow because it executes 20,000 separate INSERT queries to the database.
