When working with data that rarely changes, caching query results can significantly improve your application's performance.
This lesson explores different approaches to implement caching in Laravel applications.
Why Use Caching?
Consider a scenario where you're generating a report of the 10 most-sold books over a specific period. If this query:
- Takes approximately half a second to execute
- Queries tens of thousands of records
- Is already optimized at the SQL/query builder level
- Doesn't need to show real-time data (updating once per day is sufficient)
This is an ideal candidate for caching. So, the query here is to get 10 most-sold book for the last 30 days:
$books = Book::join('book_order', 'books.id', '=', 'book_order.book_id') ->join('orders', 'book_order.order_id', '=', 'orders.id') ->whereRaw('orders.created_at BETWEEN "' . now()->subDays(30)->format('Y-m-d H:i:s') . '" AND "' . now()->format('Y-m-d H:i:s') . '"') ->selectRaw('books.*, SUM(book_order.quantity) AS books_sold') ->groupBy('books.id') ->orderBy('books_sold', 'desc') ->take(10) ->get();In the database, I have 50,000 books and 100,000 orders. The query takes about 120ms. While the query is pretty fast now, with millions of records, it could take seconds to load, especially in production.
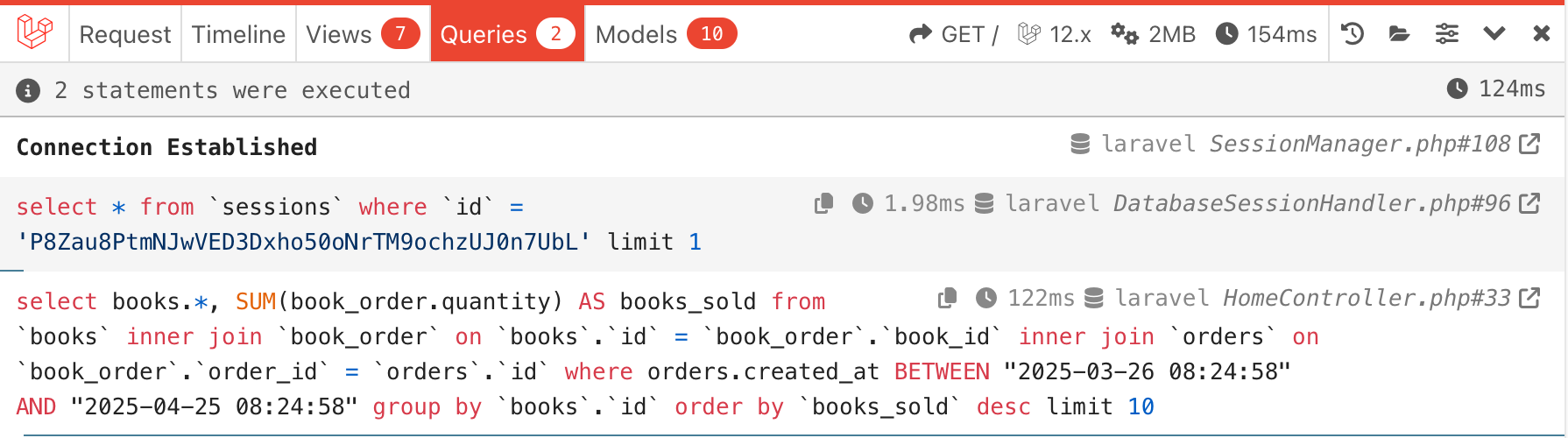
Caching The Query
The simplest way to implement caching is using...
