In the first lessons, we relied on the users.is_admin column to define permissions. But what if there are more than two roles? Then you probably need to create a separate DB table, roles, and add a users.role_id column with a foreign key. This is precisely what we will cover in this lesson.
Imagine we have three roles:
- Simple user: can only view the list of tasks
- Administrator: can do everything with tasks - view/create/update/delete
- Manager: can only view and update tasks created by the administrator
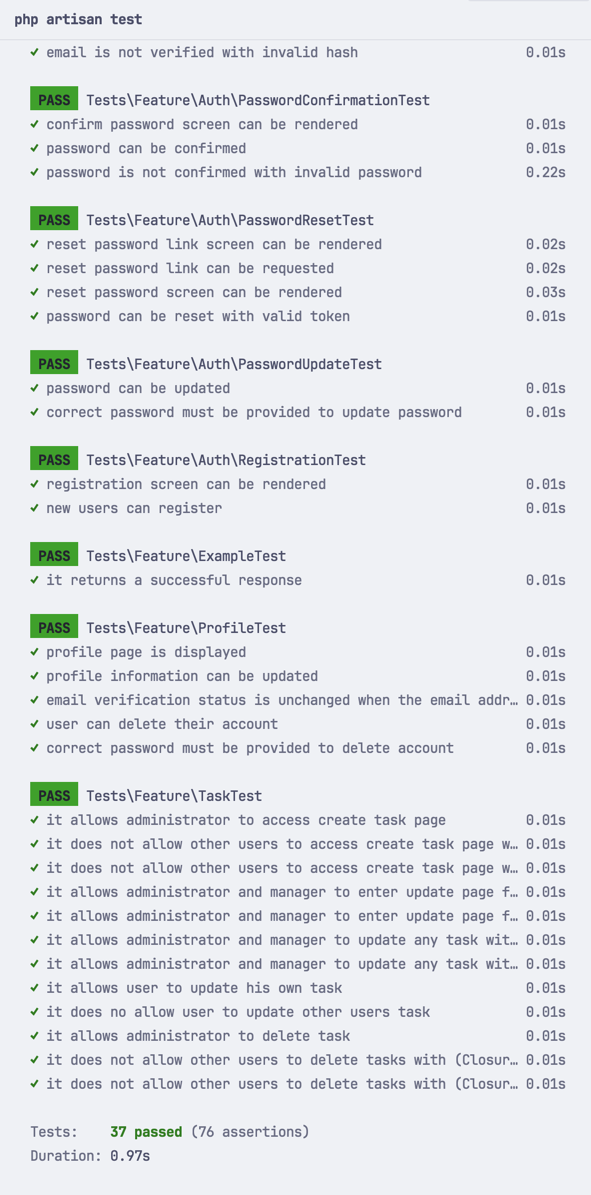
As usual, by the end of the lesson we will have a repository with automated tests, including the ones from default Laravel Breeze:
The Key Point: Policy
We will continue on the example of the last lesson, where the main logic is inside of TaskPolicy. By the end of this lesson, we will change the conditions here. Our starting point is this:
app/Policies/TaskPolicy.php
class TaskPolicy{ public function create(User $user): bool { return true; } public function update(User $user, Task $task): bool { return $user->is_admin || $task->user_id === $user->id; } public function delete(User $user, Task $task): bool { return $user->is_admin || $task->user_id === $user->id; }}Let's change that $user->is_admin to something more flexible.
Migrations and Models for Separate Roles Table
Migration
Schema::create('roles', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->string('name'); $table->timestamps();});app/Models/Role.php
class Role extends Model{ use HasFactory; protected $fillable = ['name'];}database/seeders/RoleSeeder.php
use App\Models\Role; // ... class RoleSeeder extends Seeder{ /** * Run the database seeds. */ public function run(): void { Role::create(['name' => 'User']); Role::create(['name' => 'Administrator']); Role::create(['name' => 'Manager']); }}And, of course, call the seeder:
database/seeders/DatabaseSeeder.php
class DatabaseSeeder extends Seeder{ /** * Seed the application's database. */ public function run(): void { $this->call(RoleSeeder::class); }}Then, we add a foreign key with...

Do you think static role IDs are ok? I mean what if someone has CRUD of roles and they delete roles and then add, what do you suggest in that case as there will be different roles IDs for same roles in that case?
Static role ID is okay if you know that roles are not editable. If they are - it's better to always query the role ID or check by name.
In a way, if a resource can switch an ID - then it can't be static, it should always be dynamic