Now let's begin to get the data from the API. In this lesson, we will create the first API endpoint to get Posts and will show them in the table by replacing the dummy hard-coded data.

Laravel Part: Posts DB Structure and API
First, we need to create a Model, Migration, Controller, and API route.
php artisan make:model Post -mdatabase/migrations/xxxx_create_posts_table.php:
public function up(): void{ Schema::create('posts', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->string('title'); $table->longText('content'); $table->timestamps(); });}app/Models/Post.php:
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Factories\HasFactory; class Post extends Model{ use HasFactory; protected $fillable = [ 'title', 'content', ];}Then we can make a Factory:
php artisan make:factory PostFactoryAnd add the following code to the PostFactory:
database/factories/PostFactory.php
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Factories\Factory; class PostFactory extends Factory{ public function definition(): array { return [ 'title' => $this->faker->word(), 'content' => $this->faker->paragraphs(asText: true), ]; }}This allows us to add a seeder:
php artisan make:seeder PostSeederIn the PostSeeder we can add the following code:
database/seeders/PostSeeder.php:
use App\Models\Post;use Illuminate\Database\Seeder; class PostSeeder extends Seeder{ public function run(): void { Post::factory(20)->create(); }}And of course, in our DatabaseSeeder, we can call the PostSeeder:
database/seeders/DatabaseSeeder.php:
// ... $this->call([PostSeeder::class]); // ...Now, we can run the migrations and seed the database. After this, we can create a controller for the API.
php artisan make:controller Api/PostControllerIn the controller for now we will just return a collection of all posts.
app/Http/Controllers/Api/PostController.php:
class PostController extends Controller{ public function index() { return Post::all(); }}And the route. Because all the routes will be for API we will add them to the routes/api.php file. This way Laravel will automatically add an api/ prefix to the routes. Before that, we must run the install:api Artisan command to prepare the Laravel application for API.
php artisan install:apiNow we have API routes:
bootstrap/app.php:
return Application::configure(basePath: dirname(__DIR__)) ->withRouting( web: __DIR__.'/../routes/web.php', api: __DIR__.'/../routes/api.php', commands: __DIR__.'/../routes/console.php', health: '/up', ) ->withMiddleware(function (Middleware $middleware) { $middleware->statefulApi(); }) ->withExceptions(function (Exceptions $exceptions) { // })->create();We can add our route.
routes/api.php:
use App\Http\Controllers\Api\PostController; Route::get('posts', [PostController::class, 'index']);Calling API from Vue
Now we can add the JS code to the PostsIndex Vue component we created earlier. All the JS code needs to go into the <script> tag.
First, we need to add a data variable where all posts will be assigned. Let's call that variable posts and assign a default value of empty array.
resources/js/components/Posts/Index.vue:
<template> // ...</template> <script>export default { data() { return { posts: [] } }}</script>Next, we will create a method fetchPosts which will make a get request to the /api/posts and will fetch all the posts.
When the request is successful, .then method will be executed. It will add all the posts from the API response to the posts data variable.
If something goes wrong, we use .catch to get any errors. For now, we will just console.log them.
And the last thing: when the components get mounted (in other words, initialized), we need to call fetchPosts() This is done in the mounted. We use the syntax of this.fetchPosts() to show that it comes from the same component.
resources/js/components/Posts/Index.vue:
<template> // ...</template> <script>export default { data() { return { posts: [] } }, mounted() { this.fetchPosts() }, methods: { fetchPosts() { axios.get('/api/posts') .then(response => this.posts = response.data) .catch(error => console.log(error)) } } }</script>In other words, three things:
- You initialize the variables in
data() - You add custom functions in
methods: - If those functions need to be called immediately, you call them in
mounted()
Now, visit the front page and open the Developer tools. In the Network tab you will see that the API request to the /api/posts was made and shows all the posts in the Response part.
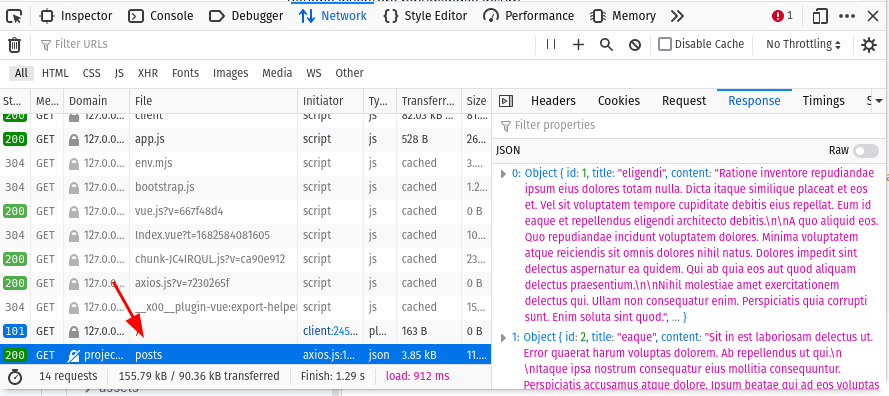
Showing API Data in Table
Now, we need to show all these posts in the table. For this we will use v-for Vue directive in the tr table row element.
Instead of hard-coded data in the table, replace it with the v-for="post in posts":
resources/js/components/Posts/Index.vue:
<template> <div class="overflow-hidden overflow-x-auto p-6 bg-white border-gray-200"> <div class="min-w-full align-middle"> <table class="min-w-full divide-y divide-gray-200 border"> <thead> <tr> <th class="px-6 py-3 bg-gray-50 text-left"> <span class="text-xs leading-4 font-medium text-gray-500 uppercase tracking-wider">ID</span> </th> <th class="px-6 py-3 bg-gray-50 text-left"> <span class="text-xs leading-4 font-medium text-gray-500 uppercase tracking-wider">Title</span> </th> <th class="px-6 py-3 bg-gray-50 text-left"> <span class="text-xs leading-4 font-medium text-gray-500 uppercase tracking-wider">Content</span> </th> <th class="px-6 py-3 bg-gray-50 text-left"> <span class="text-xs leading-4 font-medium text-gray-500 uppercase tracking-wider">Created at</span> </th> </tr> </thead> <tbody class="bg-white divide-y divide-gray-200 divide-solid"> <tr v-for="post in posts"> <td class="px-6 py-4 whitespace-no-wrap text-sm leading-5 text-gray-900"> {{ post.id }} </td> <td class="px-6 py-4 whitespace-no-wrap text-sm leading-5 text-gray-900"> {{ post.title }} </td> <td class="px-6 py-4 whitespace-no-wrap text-sm leading-5 text-gray-900"> {{ post.content }} </td> <td class="px-6 py-4 whitespace-no-wrap text-sm leading-5 text-gray-900"> {{ post.created_at }} </td> </tr> </tbody> </table> </div> </div></template> <script>// ...</script>That post in posts means that it takes posts variable from the component's <script> part, and performs a loop, assigning every element to the post variable. It's equivalent of PHP foreach ($posts as $post).
Now, after visiting the page, you should see the table with all the posts that are fetched from the API.


One suggestion: As you are writing a text based tutorials, pages are getting longer. So in that case, please add a scroll to top button, I feel it really necessary
Good suggestion, will add to the to-do list.